What is the Difference between Perlite And Vermiculite

Are you trying to improve your garden or indoor plants but feeling confused about which soil additive to use? You’ve probably come across perlite and vermiculite, two popular options that seem similar but work very differently.
Knowing the difference between perlite and vermiculite can make a huge impact on your plants’ health and growth. You’ll discover exactly what sets these two apart and how to choose the right one for your needs. Keep reading—your plants will thank you!
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/SPR-vermiculite-vs-perlite-6455754-hero-1a2d3e14e0584fbaa4a990ebef1d494b.jpg)
Credit: www.thespruce.com
Perlite Basics
Perlite is a popular material used in gardening and construction. It is known for its light weight and ability to hold air and water. Understanding perlite basics helps you choose the right material for your needs. Below are key facts about perlite’s origin, physical features, and uses.
Origin And Formation
Perlite forms from volcanic glass. When lava cools quickly, it traps water inside. Heating this glass causes it to expand like popcorn. This process creates small, lightweight white particles. These particles have a porous texture that holds air and moisture well.
Physical Properties
Perlite is white and very light. Its surface is rough and porous. These pores trap air and water, helping plants breathe and grow. Perlite does not break down easily. It is also sterile, so it does not carry diseases or pests.
Common Uses
Gardeners mix perlite with soil to improve drainage and aeration. It helps roots get oxygen and keeps soil from becoming too wet. Builders use perlite in lightweight concrete and insulation. It also appears in hydroponic systems as a growing medium.
Vermiculite Basics
Vermiculite is a popular material in gardening and construction. It helps improve soil and keeps plants healthy. Understanding vermiculite basics is important for anyone interested in gardening or soil care.
This section explains what vermiculite is, where it comes from, its physical traits, and its common uses.
Origin And Formation
Vermiculite forms from minerals that heat up deep inside the Earth. It comes from mica, a natural rock. When heated, vermiculite expands like tiny worms or flakes. This expansion creates its lightweight and absorbent nature.
Physical Properties
Vermiculite looks like small, shiny flakes. It is light and soft to touch. It holds water well and keeps air flowing in the soil. Vermiculite does not break down quickly. It also resists heat and fire.
Common Uses
Gardeners mix vermiculite into soil to keep it moist and loose. It helps plant roots grow better. Builders use vermiculite for insulation and fireproofing. It also works in packaging to protect fragile items.
Comparing Physical Traits
Perlite and vermiculite are common soil additives. They help plants grow better by changing the soil’s physical traits. These traits affect how water moves, how air flows, and how roots grow. Understanding their differences helps gardeners choose the right one.
Texture And Appearance
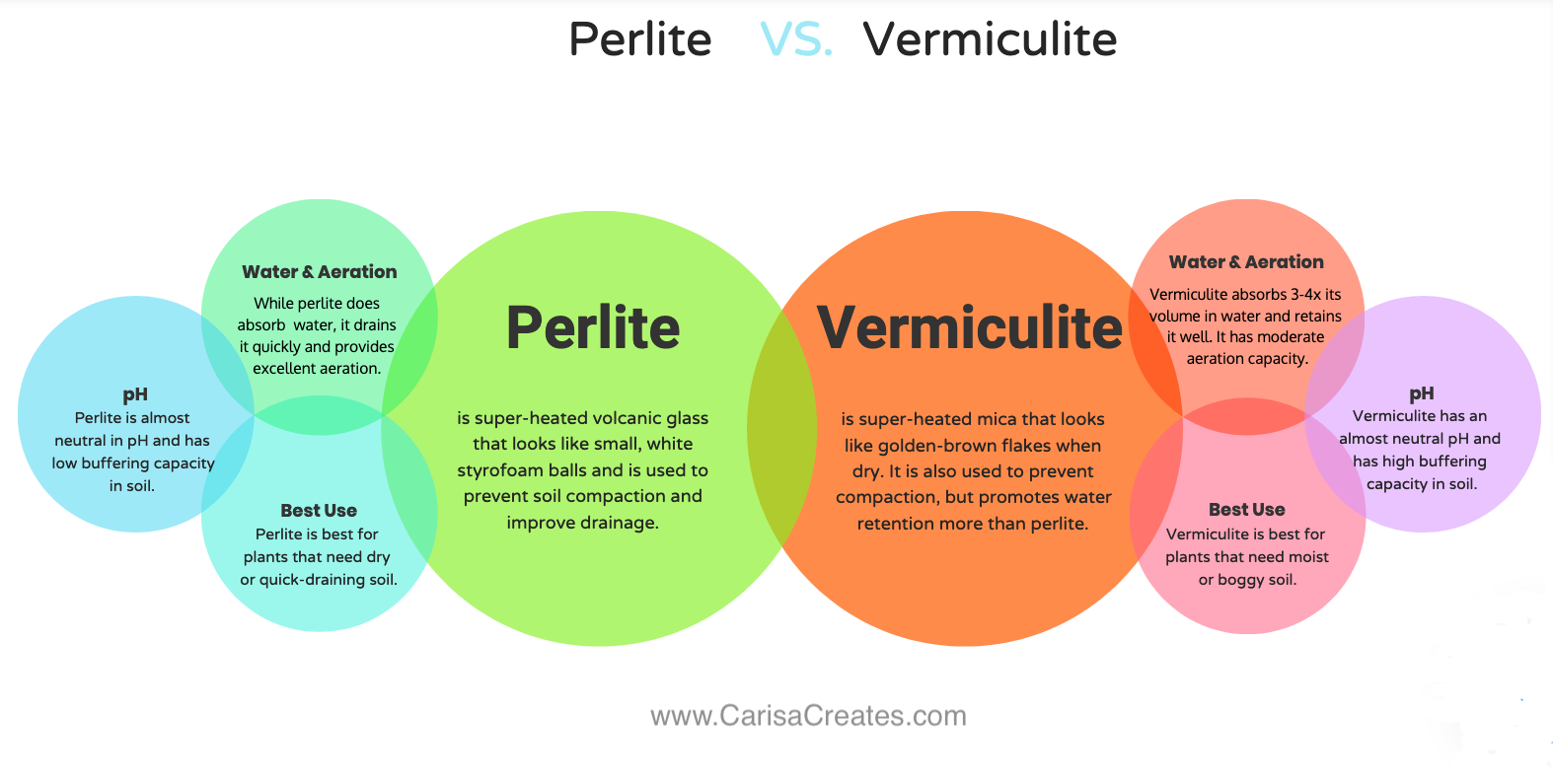
Perlite looks like small white balls or granules. It feels rough and hard to touch. Vermiculite has a shiny, layered look. It feels soft and crumbly. Perlite is lightweight and porous. Vermiculite is denser and feels spongy.
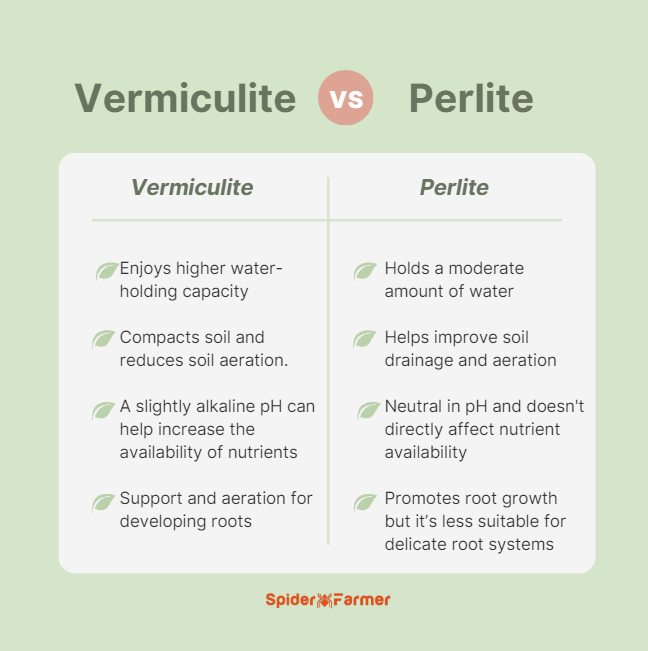
Water Retention
Perlite holds little water. It lets water drain quickly from soil. Vermiculite absorbs and holds much more water. It keeps moisture near plant roots longer. This makes vermiculite good for plants needing steady moisture.
Aeration Qualities
Perlite creates many air pockets in soil. This helps roots get oxygen easily. Vermiculite also adds air but less than perlite. It holds more water, so air spaces are fewer. Perlite is best for plants needing good airflow.
Gardening Benefits
Both perlite and vermiculite offer unique benefits in gardening. They help improve soil and support plants in different ways. Understanding these benefits helps gardeners choose the right material for their needs.
Soil Improvement
Perlite helps loosen heavy soil. It stops soil from becoming compacted. This allows roots to breathe and grow better. Vermiculite improves soil by holding water and nutrients. It keeps the soil moist for longer. Both materials help create a better environment for plants.
Plant Growth Support
Perlite supports plant growth by providing oxygen to roots. Roots stay healthy and strong. Vermiculite holds water and nutrients close to roots. This helps young plants grow faster. Both materials make sure plants get what they need to thrive.
Drainage Effects
Perlite improves drainage by letting water flow through soil easily. It prevents water from pooling around roots. Vermiculite holds water but still allows some drainage. It keeps soil moist but not soggy. Choosing the right one depends on how much drainage plants need.
Industrial Applications
Perlite and vermiculite have many industrial uses beyond gardening. Both minerals are valued for their unique physical traits. Their lightweight and porous nature make them useful in different fields. Understanding their industrial applications helps choose the right material for specific needs.
Construction Uses
Perlite is common in construction. It mixes with cement to make lightweight concrete. This concrete is easier to handle and insulates well. Vermiculite also improves concrete by making it fire-resistant. Builders use vermiculite to fill blocks and panels. Both minerals reduce the overall weight of building materials.
Insulation Properties
Perlite and vermiculite serve as good insulators. Perlite is often found in loose-fill insulation for walls and roofs. It traps air, slowing heat loss. Vermiculite withstands high temperatures, ideal for furnace insulation. It also helps in soundproofing spaces. Each mineral adds value by improving energy efficiency in buildings.
Other Industries
Perlite appears in industrial filters and cryogenic insulation. It filters liquids in food and chemical production. Vermiculite finds use in packaging fragile items. Its cushioning protects sensitive goods during transport. Vermiculite also supports seed germination in agriculture. Both minerals fit many roles beyond their common uses.
Credit: carisacreates.com
Environmental Impact
Understanding the environmental impact of perlite and vermiculite helps gardeners choose wisely. Both materials affect the earth differently during mining, processing, and disposal. Knowing their sustainability and recycling options shows their true footprint on nature.
Sustainability
Perlite is a natural volcanic glass. It expands when heated, making it useful for soil. Mining perlite causes land disturbance and uses energy. Vermiculite is a mineral that expands with heat too. It comes from mica deposits. Mining vermiculite also affects the environment but less energy is needed for processing. Both materials are non-renewable resources. Using them responsibly means minimizing waste and choosing products from companies with good environmental practices.
Recycling And Disposal
Perlite is lightweight and does not break down easily. It can be reused in gardens or compost. Vermiculite breaks down slower in soil but can also be reused. Neither material is harmful if disposed of in landfills. Recycling options are limited, so reusing is best. Avoid throwing them away in large amounts to reduce landfill waste. Proper disposal and reuse help lower their environmental footprint.
Choosing Between Perlite And Vermiculite
Choosing between perlite and vermiculite depends on your gardening needs. Both are popular soil amendments but serve different purposes. Understanding their uses, costs, and availability helps make the best choice for your plants.
Best Uses For Each
Perlite is great for improving soil drainage and aeration. It prevents soil from becoming too compact. Use it in potting mixes for cacti, succulents, and orchids. Vermiculite holds water well and keeps soil moist. It works best for seed starting and moisture-loving plants. Gardeners often mix vermiculite into soil to help with nutrient retention.
Cost Considerations
Perlite usually costs less than vermiculite. It is lightweight and easy to ship, reducing delivery fees. Vermiculite tends to be pricier due to its water-holding properties. Buying in bulk can lower costs for both materials. Think about how much you need before purchasing.
Availability Factors
Perlite is widely available in garden centers and online. It comes in different grades for various uses. Vermiculite is also easy to find but may be less common in some regions. Some stores stock only one type, so check availability locally. Both materials are safe and natural for gardening.
Credit: spiderfarmer.eu
Conclusion
Perlite and vermiculite both improve soil but work differently. Perlite helps with drainage and keeps soil light. Vermiculite holds water and adds nutrients to soil. Choose perlite for plants needing dry roots. Pick vermiculite for plants that like moisture. Knowing these differences helps your plants grow healthy.
Simple choices make a big difference in gardening success. Keep these tips in mind for better plant care.






